Writing Out a Musical Transposition - How to Transpose Music to a New Key
Transposition often takes place during the act of making music or performing, but it can also be written out either as transposed chords or as a fully notated piece of music.
For most people who are new at the skill of transposing, the first question is simply, How do I transpose? That’s where we will begin.
A recap for clarification: transposition is the process of changing a piece of music from the key it is currently written or performed in to a different key that someone prefers. The pitches of the notes will change, but the rhythm will remain the same. There are many different reasons for transposing. For singers, it might be to pitch the song in a key that suits their individual voice better; it might be to make a song more comfortable and appealing when a large group (such as a church congregation) sings in unison. Some might transpose to make life easier for the musicians who will play the piece on their instruments, since some keys seem to be easier on certain instruments than others are; or someone might need to write out a part for a transposing instrument (that is, an instrument such as a clarinet or trumpet which plays a concert pitch that is different from the notated pitch). And transposition might simply be done as an exercise in musicianship, for learning and practicing music theory.
A Piece in the Original Key of E Major

Step One
The two initial questions are: Do you want to raise or lower the pitch? and, By how much (what interval)?
Do you want the new key to sound higher than the previous one? Does it need to be a lot higher or just a little?
When you know direction and distance (interval), you will simply change each note or chord in the specified direction and for the given distance. Sounds simple. But there are some caveats to share. When we move from one letter of the music alphabet to the next in sequence (both unaltered, i.e. natural) the interval is frequently a whole step (= two half-steps) or major second (M2). But between two pairs (B-C and E-F) the interval is a half step. That one little fact affects all other possible intervals, so you need to be aware of it.
Sidebar for Singers
One rule of thumb that may be very helpful for singers is that it’s usually advisable to change the pitch of a song no more than a third higher or lower than the original. That sounds like a small interval, but it actually covers a lot of territory. This rule of thumb assumes that the original key was a singable one, and that the new key is intended for singers! If the original key was geared towards an instrument rather than a voice (for example, if the song was written for a beginning piano student), then that rule of thumb should probably be ignored.
Keep in mind that some people may use expressions like "I prefer to sing in the key of ___" when they ask you to transpose. That is probably because they have had good experiences with songs that were in that key. However, the name of a key by itself does not automatically tell anyone the range of the notes to be sung. That is a different issue, and it is explored and explained in two other articles I have written: "The 'Key' to Great Congregational Singing" and "One Method of Finding the Right Key." If anyone asks you to transpose to a specific key, rather than requesting a specific interval up or down, you may have to exercise some diplomacy to figure out whether they understand that the key may not end up quite as they would like it to be. One way to do that would be first to transpose only a representative portion of the music (preferably representing some of the middle range and some of the extremes), and then ask them to sing that bit to see "whether you are doing it right."
On the other hand, different keys actually do promote different feelings, according to some music scholars. Mozart was very adamant about the affect or mood of various keys, and numerous scholarly treatises have been written about the subject. It may be that the person requesting a specific key actually has a sophisticated understanding of music and is genuinely interested in hearing the colorations associated with that key, rather than finding a singable range of notes. In that case, go with the requested key.
Transposing on a Keyboard Instrument
Same Piece Transposed to Bb Major

Step Two - Think in the New Key
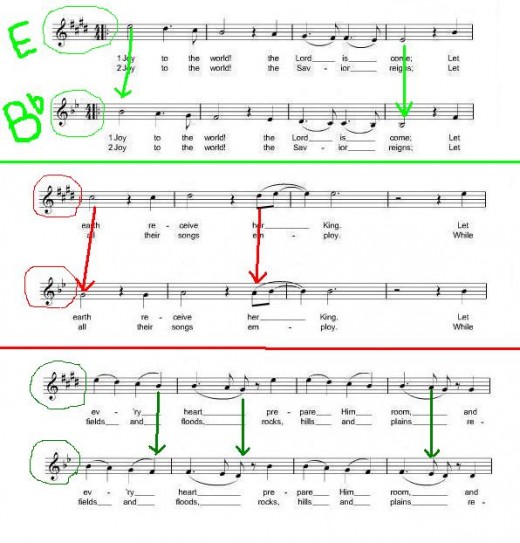
When you transpose a piece of music, whether it is a simple song for a children’s choir, a fanfare for a trumpet, or an entire score for orchestra, you will find the whole task much simpler, and actually truer to the basic concepts of music, if you start out by thinking about the new key as a whole, not just one note at a time. If you are transposing from the key of E major to the key of Bb major, for example, you will be moving from four sharps in the key signature to two flats. To orient yourself, first name the notes of the old scale, then of the new one:
E F# G# A B C# D# E
Bb C D Eb F G A Bb
Every original E will become a Bb, every B (in key of E) will become F (in Bb), etc., always using the correct octave. If you get stuck at any point, think of the scale degree of the original note; the new note in the transposed key will be the same scale degree in the new key. In the key of E, G# is the third degree of the scale. So the transposed note (in Bb) will be the third degree, or D.
A Helpful Trick
When you are writing out a transposition, you may be able to take a little shortcut to speed up the process without having to first think carefully about each and every note. (If you do this, be sure then to go back to double-check and correct any errors.) This little trick is simply to transpose by an appropriate number of lines or spaces. So, if you are raising the song by a third, write every line note of the original on the next line higher in the new key; write every space note of the original on the next space higher in the new key. You may already see the problem here: this does not take into account the locations on the staff where the line-space movement represents only a half-step, not a whole step. (Remember the B-C and E-F half-steps mentioned above?)
If you start first of all by writing the new key signature at the beginning of the staff, it can help remind you to watch for places where you may need to adjust by adding sharps, flats, or naturals.
Especially for Guitarists
Comparison of Notes, Transposing E Major to Bb Major
Reminders and Encouragement
Always watch for accidentals - sharps, flats, and naturals that are not in the key signature - and be sure to adjust appropriately for them. If an original note was sharped, then the corresponding note in the new key just needs to be raised a half-step, and that may or may not be a sharp, If an original note was flatted, the same note in the new key would be lowered a half step from what the key signature would call for.
If you are transposing for instruments, check ahead to be sure you know the actual (available) range of the instrument, so that you don't try to give the musician a note that is impossible for the instrument! Also remember that some instruments are relatively easy to adjust, if you get the key wrong. (A guitar, for example, could capo up - to a higher key - from the written key.)
Train Yourself
Practice transposing often - more often than you think you need to. Start by selecting a simple song and transposing it to many different keys. Think of who might sing the song in that key. Or transpose it for a specific transposing instrument - for example, for French horn (an F instrument - it sounds a 5th lower than written), soprano clarinet or trumpet (Bb - sounds a major second lower than written), alto saxophone (Eb - sounds a major 6th lower than written).
Start with melody only. If the harmony is fairly simple, try it too. Work one measure at a time and check yourself periodically.
Try to transpose something every day, even if you are not required to. It will help you to develop as a musician.
Available Right Here from Amazon
More Information About Transposing
- The "Key" to Great Congregational Singing
Finding the best musical key for group singing can be a challenge, but it can be a pleasant and rewarding challenge. Numerous factors determine the best key for a given song. - One Method of Finding the Right Key
A choir director/song leader needs to be aware of numerous factors that affect the quality of worship. When the vocal range of a song is poorly suited to the group, singing and worship will suffer. - How to Transpose Music, Part I: Definition - Types -...
Transposition is a very valuable skill for any musician, and it can make the difference between working well with other musicians and being something of a musical loner or a drag. - How to Transpose Music, Part II: More Tips on Playin...
Start with simple songs of only about 8-20 measures of music. As you gain skill and confidence, try the same (following) process on longer pieces.







